Architecture
Laïka as the first Layer 2 truly based on Doge
Laïka leverages a hybrid L2 architecture, combining Plasma Chain and Rollup techniques to achieve its goals of high-throughput transactions and robust security.
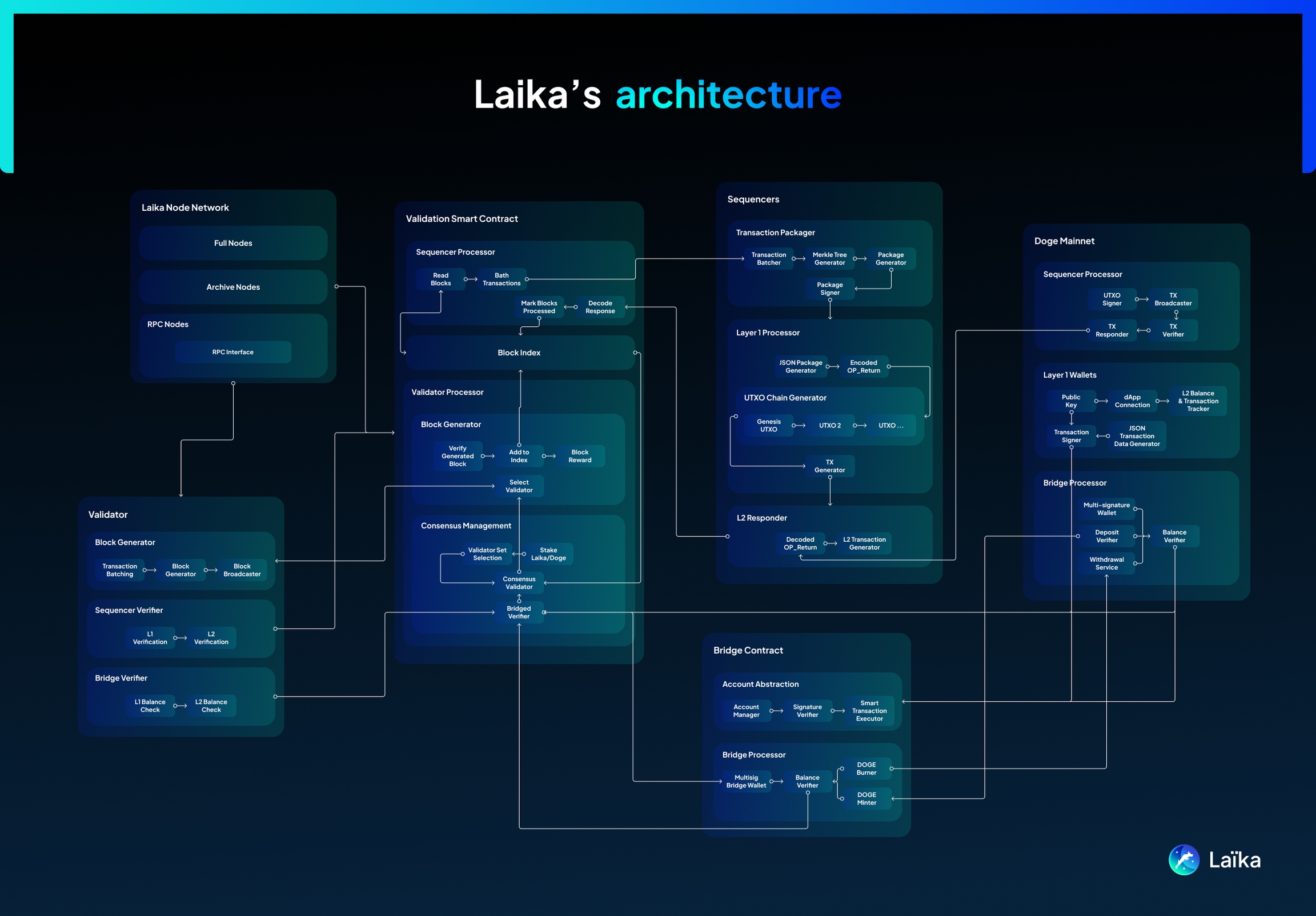
Laïka operates its own consensus protocols (Proof of Stake), transaction details are written by the Sequencers along with ZK proofs to the Dogecoin network, these proofs are then further validated by Validators on Laïka with their own Proofs which are compared to validate the data integrity. In case of any integrity loss, Laïka immediately halts operations to ensure network security. Blocks are considered truly finalized only when their details are submitted to the Dogecoin blockchain and their proofs are validated on Laïka. This mechanism reinforces the reliability and security of the network, safeguarding against potential compromises.
Laïka's key components
This section provides a high-level overview of the key components and their interactions within the Laïka network.
↝ Layers and Interaction
Laïka operates across two layers:
Layer 1 (L1): The Dogecoin blockchain serves as the L1 base layer, providing security and finality for Laika transactions.
Layer 2 (L2): The Laïka network handles high-speed transaction processing, offering significant performance improvements over L1.
↝ Key Components
Laïka's architecture comprises the following crucial components:
Smart Contracts: Deployed on the Laïka network, these contracts are essential for governing network logic, tracking state data, and enforcing security measures. They are responsible for transaction verification and ensure that data from Laïka actions can be verified on Dogecoin. Furthermore, they supports on-chain governance, allowing token holders to participate in decision-making through Laika token voting.
Validators: Responsible for validating Laïka transactions based on the consensus mechanism. They participate in block production and verify the work done by sequencers.
Sequencers: Act as intermediaries, bridging the gap between L2 and L1. They are responsible for:
Direct Network Interaction: Reading and writing data to both Laïka and Dogecoin full nodes, enabling real-time synchronization.
Verifiable Transactions: Including data for validated Laïka blocks within Dogecoin transactions, employing techniques like Merkle Trees and ZK proofs for efficient verification.
Balancing Efficiency: Aiming to bundle multiple Laïka transactions into a single Dogecoin transaction to optimize network usage.
